High Lactic Acid
High Lactic Acid is a naturally occurring organic compound with extensive applications across multiple industries. Notably, concentrations, particularly at levels reaching 2000, play a crucial role in biochemical processes, industrial manufacturing, and various commercial products. Therefore, this article provides a detailed explanation, its properties, uses, and significance in different domains.
High Lactic Acid: Comprehensive Overview
Lactic acid (C₃H₆O₃) is a carboxylic acid featuring a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to a carbonyl (-COOH) functional group. In fact, it exists in two optical isomers: L-lactic acid and D-lactic acid, both of which influence metabolic and industrial functions differently. Moreover, the content, particularly at a concentration of 2000, signifies an increased presence of this compound within a given solution or medium.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Molecular Weight: 90.08 g/mol
- Density: Approximately 1.206 g/cm³ at 20°C
- Melting Point: 53°C (solid form)
- Boiling Point: 122°C at 15 mmHg
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, ethanol, and methanol
As a result, a high concentration of lactic acid at 2000 alters its physicochemical properties, significantly impacting viscosity, reactivity, and stability within formulations.
Biological Role and Metabolic Functions
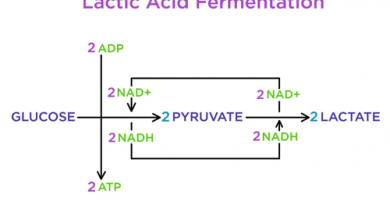
Lactic acid plays an essential role in cellular metabolism, primarily through anaerobic respiration. Specifically, during glycolysis, glucose undergoes breakdown, producing pyruvate, which subsequently converts in the absence of oxygen. Consequently, this process, known as fermentation, occurs in muscle cells, red blood cells, and specific bacterial strains.
Furthermore, elevated lactic acid levels in biological systems may result in lactic acidosis, a condition characterized by an excessive accumulation in the bloodstream, potentially leading to metabolic imbalance. However, in controlled environments, concentrations contribute to energy metabolism and cellular regulation.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
High lactic acid concentrations, particularly at 2000, have extensive applications in multiple sectors, including:
- Food Industry
- Used as a natural preservative and pH regulator in fermented products such as yogurt, pickles, and sourdough bread.
- Additionally, it enhances flavor, texture, and shelf life in processed foods and beverages.
- Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Sector
- Integral in intravenous fluids, wound healing solutions, and skin-care formulations.
- In addition, it is incorporated into topical creams and serums for its exfoliating and anti-aging properties.
- Cosmetic and Personal Care
- Acts as a key ingredient in chemical peels, moisturizers, and anti-wrinkle treatments.
- Moreover, it helps maintain skin hydration by improving moisture retention.
- Polymer and Bioplastics Manufacturing
- Essential in producing polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable plastic derived from lactic acid fermentation.
- Therefore, it is used in sustainable packaging, medical implants, and disposable cutlery.
- Agriculture and Animal Feed
- Added to silage to enhance fermentation, prolong storage life, and improve nutritional value.
- Furthermore, it functions as a microbial growth inhibitor, preventing spoilage.
- Textile and Leather Industry
- Utilized in leather tanning to soften and preserve hides.
- In addition, it helps in dyeing processes by improving color absorption.
High Lactic Acid in Fermentation and Biotechnology
In biotechnology, lactic acid fermentation serves as a fundamental process in producing bio-based chemicals. Specifically, certain bacterial strains, such as Lactobacillus, ferment carbohydrates, yielding at high concentrations. As a result, maintaining a concentration of 2000 in fermentation systems ensures optimal microbial activity, product yield, and purity.
Additionally, genetically engineered microorganisms enhance lactic acid production by increasing metabolic efficiency, reducing by-product formation, and optimizing resource utilization. Consequently, this approach enhances industrial efficiency while minimizing waste.
Physiological Effects and Health Considerations
While high lactic acid concentrations offer numerous benefits, excessive accumulation in biological systems can lead to several physiological concerns, including:
- Muscle Fatigue: Elevated lactic acid levels contribute to temporary muscle soreness during intense exercise.
- Metabolic Acidosis: Overproduction or impaired clearance may result in a decrease in blood pH, affecting organ function.
- Lactate Threshold: The body regulates production and clearance to sustain endurance performance.
Analytical Techniques for Measuring High Lactic Acid Levels
Several methods exist for quantifying lactic acid concentrations, ensuring accuracy and consistency in industrial and clinical applications. Accordingly, these methods include:
- Enzymatic Assays: Utilize lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) for precise measurement.
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Separates and quantifies lactic acid in complex mixtures.
- Spectrophotometry: Detects based on optical absorbance changes.
These analytical techniques are critical in monitoring levels in food, pharmaceuticals, and metabolic research. Moreover, accurate measurement ensures product quality and safety.
Environmental and Sustainability Aspects
Lactic acid, especially in biodegradable forms like PLA, offers sustainable alternatives to petroleum-based plastics. Consequently, the ability to produce HLA concentrations through fermentation reduces environmental impact by:
- Lowering carbon footprint associated with synthetic polymer production.
- Promoting circular economy models where bio-based materials degrade naturally.
- Enhancing waste valorization through efficient bioconversion processes.
PT. Samiraschem Indonesia is Reliable Supplier and Distributor Lactic Acid with High Quality Product and Good Price. We are Serving and Delivered Area such Jakarta Bandung Semarang Jogja Surabaya Medan and Batam
High lactic acid concentrations, particularly at 2000, have profound implications in biochemistry, industrial applications, and environmental sustainability. From food preservation to biodegradable plastics, its versatility makes it an indispensable compound. As a result, understanding its properties, production methods, and physiological impact ensures optimized utilization across diverse fields.