Dibasic Ester Structure
Dibasic esters (DBE) refer to a class of chemical compounds that are esters of dicarboxylic acids. They are often used as solvents in various industrial applications, such as coatings, paints, and polymers. The general structure consists of two functional groups attached to a dicarboxylic acid backbone.
Dibasic Ester Structure
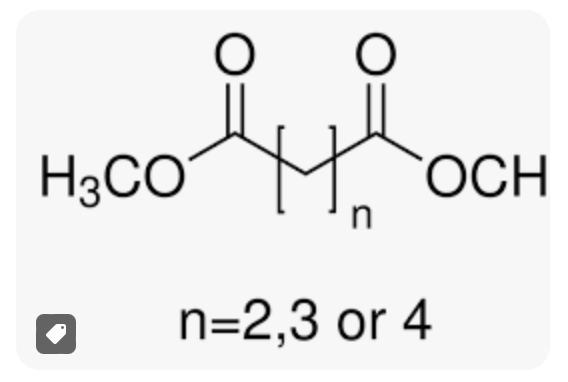
One of the common examples of dBE is the mixture of esters of adipic, glutaric, and succinic acids. Here’s a structural representation of the components:
Adipic Acid Ester (e.g., Dimethyl Adipate)
Adipic-acid-ester refers to the ester derivative of adipic acid. Adipic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the formula HOOC-(CH2)4-COOH. When esterified, it forms esters, typically with alcohols. The most common adipic acid ester is dimethyl adipate, formed by the esterification of adipic acid with methanol.
Glutaric Acid Ester (e.g., Dimethyl Glutarate)
Glutaric acid ester refers to the ester derivative of glutaric acid, which is a dicarboxylic acid with the formula HOOC-(CH2)3-COOH. When esterified, it forms esters, typically with alcohols. The most common glutaric acid ester is dimethyl glutarate, formed by the esterification of glutaric acid with methanol.
Succinic Acid Ester (e.g., Dimethyl Succinate)
Succinic acid ester refers to the ester derivative of succinic acid, which is a dicarboxylic acid with the formula HOOC-(CH2)2-COOH. When esterified, it forms esters, typically with alcohols. The most common succinic acid ester is dimethyl succinate, formed by the esterification of succinic acid with methanol.
In these Dibasic Ester Structure :
- The
O=C-O-groups are the ester linkages. - The
(CH2)ngroups represent the aliphatic chains of the dicarboxylic acids, withnvarying depending on the specific acid.
Dibasic esters are valued for their biodegradability and low toxicity, making them suitable for environmentally friendly solvent applications.






